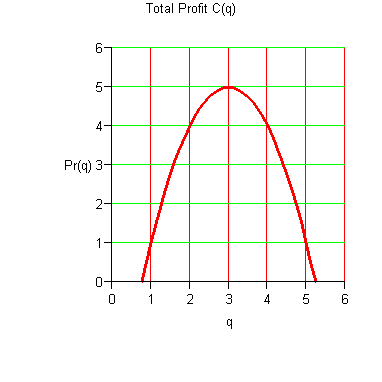
Marginal Analysis Criterion for Maximal Average Profit Closely related to Marginal Analysis for Minimum Average Cost . Not quite the same as Marginal Analysis Criterion for Maximum Profit . Hoffmann/Bradley, p. 242 Let P(q) is the total profit of producing the first q units. Here is the graph of a typical P(q).
- ·
- The graph of P(q) is smooth and concave downward.
- ·
- P(q) = 0 has exactly two positive roots, the smallest is called the break even point .
|
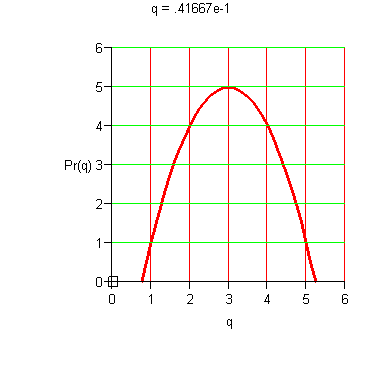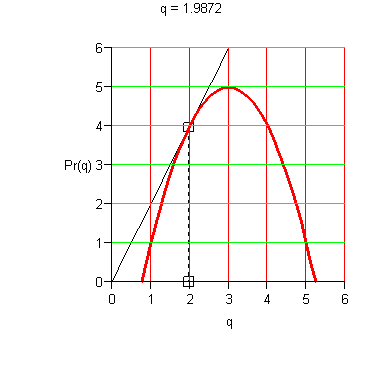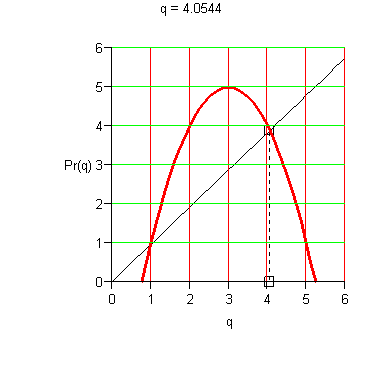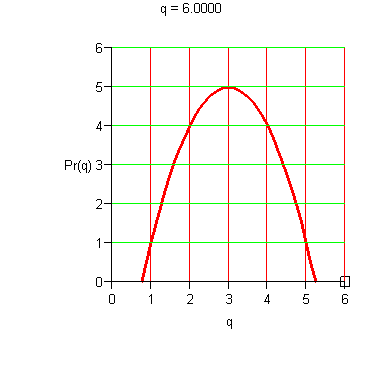
Marginal Analysis Criterion for Maximal Average Profit. Average profit per unit is maximized at the level of production where the average profit per unit equals the marginal profit; that is
|
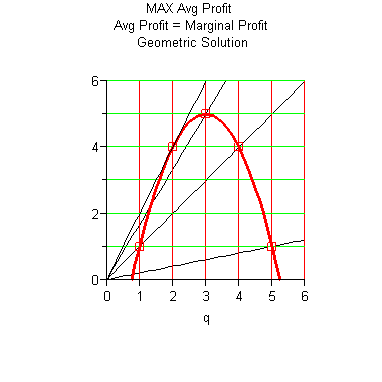
|
|
File translated from TEX by TTHgold, version 4.00.
On 03 Sep 2011, 21:26.