|
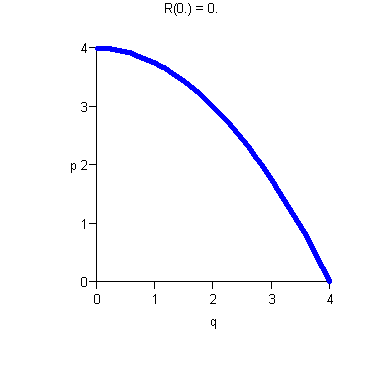
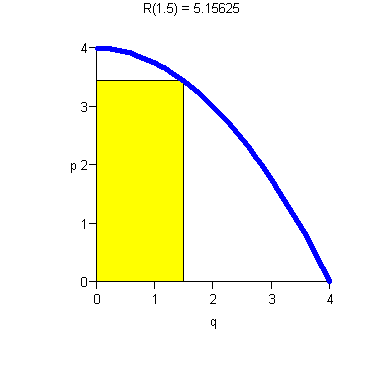
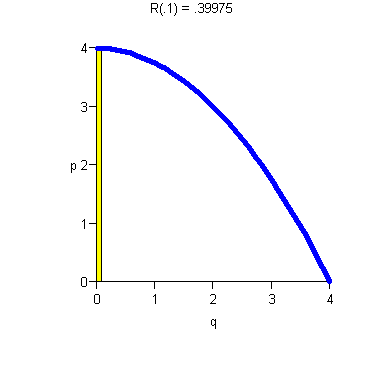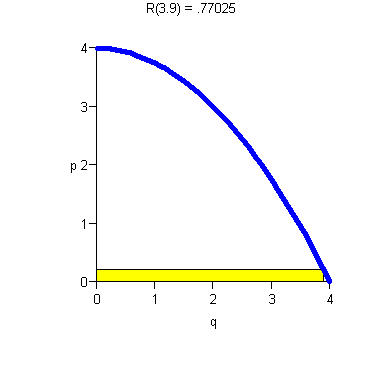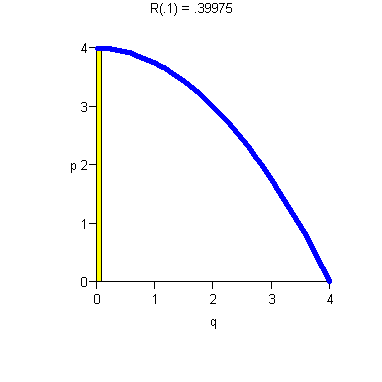
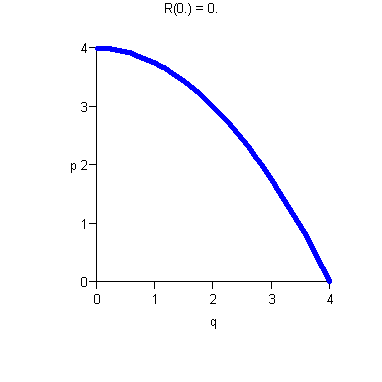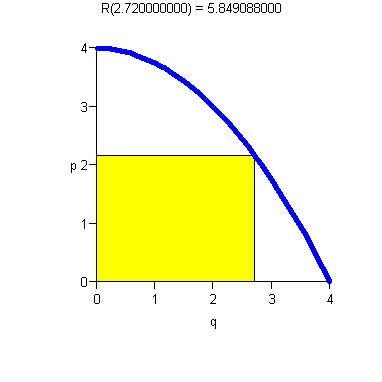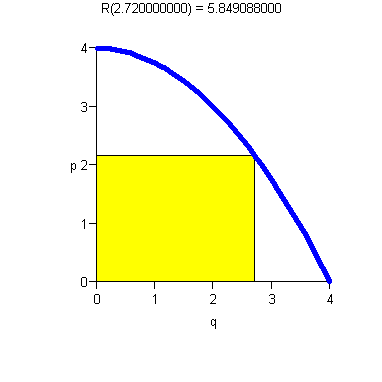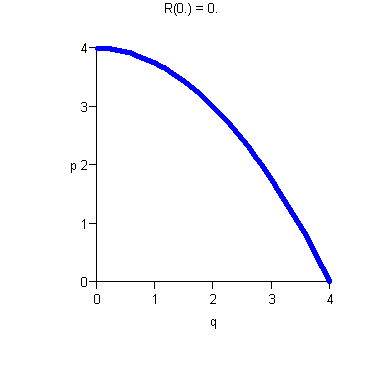
- ·
- Increasing p means decreasing demand.
- ·
- There is maximum price D(0) the consumer will pay.
- ·
- There is maximum consumer demand (In our example, q = 4).
File translated from TEX by TTH, version 3.85.
On 23 Feb 2009, 21:45.
| Math 165: Maximizing Revenue |
| PDF Version for Printing: 165maxrev.pdf |
|



