I. Definitions
- 1.
- Define (ϵ-δ): limx → a f(x) = L.
- 2.
- Define: limx → a− f(x) = L.
- 3.
- Define: The function f is continuous at a.
- 4.
- Define: The function f is differentiable at a.
- 5.
- Define: The set of numbers A is bounded above.
- 6.
- Define: The number b is the least upper bound of a set of numbers A.
- 7.
- Define: The domain of a function f.
- 8.
- (See chap5cproj) Is the following "definition" correct? Explain your answer!
Definition HH.
|
- 9.
- Give an example of two functions f and g such that f ° g = g ° f. Be sure to verify that the domains are the same.
- 10.
- Give an example of a bounded function f defined for all real numbers such that limx → 0f(x) does not exist.
- 11.
- Give an example of a bounded set of numbers A which has a least element. Give the greatest lower of this set A [infA].
- 12.
- Give an example of a nonempty bounded set of numbers A which has no least element. Give the greatest lower bound of this set A.
- 13.
- Give an example of a nonempty bounded set AQ of rational numbers whose least upper bound is not a rational number .
- 14.
- Give an example of a function f, defined on [0,1], such that
- •
- f is continuous on [0,1] and differentiable on (0,1),
- •
- f′(x) ≠ 0 for all x in (0,1).
- 15.
- Give an example of a function f with domain (0,1) such that
- •
- f is continuous on (0,1) and
- •
- f is not bounded above on (0,1).
- 16.
- Give an example of a function f with domain [0,1] such that
- •
- f is continuous on [0,1] except at x = [1/2] and
- •
- f is not bounded above on [0,1].
- 17.
- Give an example of a function f with domain [0,1] such that
- •
- f is continuous on [0,1] except at x = [1/2] and
- •
- f is bounded above on [0,1], and
- •
- f does not assume a maximum value on [0,1].
- 18.
-
If f is a bounded function defined on [0,1],
define
Give an example of a pair of functions, f,g, such thatinf
f ≡
inf
x ∈ [0,1]f(x). inf
f + inf
g < inf
(f + g).
- 19.
- Give an example of a function f such that
- •
- f is continuous for all real numbers,
- •
- f is not differentiable at a = 1.
- 20.
- Find the decimal and binary expansions of x = [1/5].
- 21.
- Express as a rational number x = [p/q], p, q natural numbers.
- •
- x = 0.bin―01 (Binary or Base 2)
- •
- x = 0.―01 (Decimal or Base 10)
- •
- x = 0.―01― (Decimal or Base 10)
- 22.
-
Using (P1 - P9), show that
− (a ·b) = (−a) ·b.
- 23.
-
Using (P1 - P12), show that
if and only if:a ≤ b For every ϵ > 0, a < b + ϵ.
- 24.
-
Prove by mathematical induction (PMI) or otherwise:
13 + …+ n3 = (1 + …+ n)2.
- 25.
- Prove (ϵ− δ):
Theorem. If
|
|
- 26.
- Let f be defined on [0,1) be such that
- •
- f is increasing on [0,1) (If 0 ≤ x1 < x2 < 1, then f(x1) < f(x2).)
- •
- f is bounded above on [0,1).
|
- 27.
-
Prove: If f is differentiable at a, then
f′(a) =
lim
h → 0f(a + h) − f(a − h) 2h.
- 28.
- State and prove Rolle's Theorem.
- 29.
- State and prove the Mean Value Theorem. You may assume Rolle's Theorem.
IV. County Line Theorem
- 30.
- Contentious County is bounded on the south by a curved road and bounded on the north by Swithchback Creek.
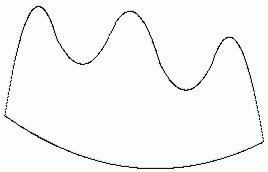
- 31.
- (Letter Grade: A - E) Write and type an essay on a topic of your choice that is very relevant to the material considered in the course. Your essay should include at least one substantial example and at least one substantial theorem and its proof.
File translated from TEX by TTH, version 4.06.
On 25 Apr 2015, 18:43.